哈希表 1. 两数之和 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution { public int [] twoSum(int [] nums, int target) { HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++){ int key = target - nums[i]; if (map.containsKey(key)){ return new int []{map.get(key), i}; } map.put(nums[i], i); } return new int []{}; } }
建立<值,序号>的哈希表,存放整数数组中每个数值即对应的序号,遍历到某个数组的时候,查找之前已存入的数值中有无符合要求的,有则return。
49. 字母异位词分组 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution { public List<List<String>> groupAnagrams (String[] strs) { HashMap<String, List<String>> map = new HashMap <>(); for (String s : strs) { int [] hash = new int [26 ]; for (char c : s.toCharArray()) { hash[c - 'a' ]++; } String key = Arrays.toString(hash); map.computeIfAbsent(key, k -> new ArrayList <>()).add(s); } return new ArrayList <>(map.values()); } }
建立哈希表存放结果,遍历字符串数组,用hash存放每个字母的频率,并转换成字符串作为哈希表的key,当已存在key时把字符串加入对应value,还未存在时则建立新的映射。
128. 最长连续序列 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class Solution { public int longestConsecutive (int [] nums) { if (nums == null || nums.length == 0 )return 0 ; else { Set<Integer>set = new HashSet <>(); for (int i : nums) { set.add(i); } int ans = 1 ; for (int n : set) { if (!set.contains(n - 1 )){ int len = 1 ; int t = n; while (set.contains(t+1 )){ len++; t++; } if (len > ans)ans = len; } } return ans; } } }
把数组加进set中,先遍历判断当前元素n是不是其所在序列的首元素(如果n-1不在set中则是首元素),对应首元素,再循环判断n的连续序列在不在set中并记录长度,直到遍历完set得到最长连续序列。
双指针 283. 移动零 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution { public void moveZeroes (int [] nums) { int beg = 0 ; for (int end = 0 ; end < nums.length; end++){ if (nums[end] != 0 ){ int t = nums[beg]; nums[beg] = nums[end]; nums[end] = t; beg++; } } } }
beg指向数组中非零元素应该放置的位置,表示的是第一个0应该被移动到的位置。end用来遍历数组中的每个元素。如果end所指元素是非零元素,就应该将它移动到数组的前面(即beg指向的位置)。
11. 盛最多水的容器 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution { public int maxArea (int [] height) { int max = 0 ; int beg = 0 ; int end = height.length - 1 ; while (beg < end){ int v = Math.min(height[beg], height[end]) * (end - beg); if (v > max) max = v; int t = Math.min(height[beg], height[end]); if (height[beg] >= height[end]){ end--; while (height[end] <= t && end-1 > beg)end--; } else { beg++; while (height[beg] <= t && beg+1 < end)beg++; } } return max; } }
开始时将两个指针放在两端,对于较大的一边,无论怎么移动容量都会变小;对于较小的一边,移动到更小或相等的值容量会一定减小,但是移动到更大的值,容量有可能变大。因此总是移动较小的一边到更大的值。注意beg一定小于end。
15. 三数之和 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> threeSum (int [] nums) { List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList <>(); Arrays.sort(nums); for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length - 2 ; i++) { if (i != 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1 ]) continue ; int left = i + 1 ; int right = nums.length - 1 ; while (left < right) { int sum = nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right]; if (sum == 0 ) { ans.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i], nums[left], nums[right])); while (left < right && nums[left] == nums[left + 1 ]) left++; while (left < right && nums[right] == nums[right - 1 ]) right--; left++; right--; } else if (sum < 0 ) { left++; } else { right--; } } } return ans; } }
42. 接雨水 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 class Solution { public int trap (int [] height) { int n = height.length; int [] preMax = new int [n]; int [] sufMax = new int [n]; int preMax_now = 0 , sufMax_now = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++){ if (height[i] > preMax_now) { preMax_now = height[i]; preMax[i] = height[i]; } else { preMax[i] = preMax_now; } if (height[n - i - 1 ] > sufMax_now){ sufMax_now = height[n - i - 1 ]; sufMax[n - i - 1 ] = height[n - i - 1 ]; } else { sufMax[n - i - 1 ] = sufMax_now; } } int sum = 0 ; for (int j = 0 ; j < n; j++){ sum += Math.min(preMax[j], sufMax[j]) - height[j]; } return sum; } }
滑动窗口 3. 无重复字符的最长子串 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution { public int lengthOfLongestSubstring (String s) { if (s == null || s.length() == 0 ) return 0 ; int n = s.length(); int max = 0 ; int right = 0 ; Set<Character> set = new HashSet <>(); for (int left = 0 ; left < n; left++) { while (right < n && !set.contains(s.charAt(right))) { set.add(s.charAt(right)); right++; } max = Math.max(max, right - left); if (right == n - 1 ) break ; set.remove(s.charAt(left)); } return max; } }
建立left、right两个指针形成一个滑动窗口,维护一个set存放窗口内字符和max存放最大字串长度。right负责遍历检查当前字符是否与窗口内部有重复,若无重复则继续向右移动,若有重复则暂停移动,更新max的值,移动left指针以收缩窗口,并将之前left指针所指字符移出集合。此时已将重复字符中的一个取出,即窗口内部都是不重复的字符,直到right指针移动到末尾。
438. 找到字符串中所有字母异位词 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution { public List<Integer> findAnagrams (String s, String p) { List<Integer> result = new ArrayList <>(); int n1 = s.length(), n2 = p.length(); if (n1 < n2)return result; int pArr[] = new int [26 ]; for (char c : p.toCharArray()){ pArr[c - 'a' ]++; } int left = 0 , right = 0 ; int tArr[] = new int [26 ]; while (right < n1){ tArr[s.charAt(right) - 'a' ]++; if (right - left + 1 == n2){ if (Arrays.equals(pArr, tArr)){ result.add(left); } tArr[s.charAt(left) - 'a' ]--; left++; } right++; } return result; } }
先判断两个序列的长度关系,如果源序列短于目标序列则肯定无法形成异位词。再用大小为26的数组构造目标序列的哈希表,记录目标序列每个字符的频率。再利用与目标序列等长的定长滑动窗口的哈希表与目标序列哈希表进行比较,若相同则为异位词,记录窗口起始位置。
子串 560. 和为 K 的子数组 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution { public int subarraySum (int [] nums, int k) { int ans = 0 ; int sum = 0 ; Map<Integer, Integer> preSum = new HashMap <>(); preSum.put(0 , 1 ); for (int num : nums) { sum += num; if (preSum.containsKey(sum - k)) { ans += preSum.get(sum - k); } preSum.put(sum, preSum.getOrDefault(sum, 0 ) + 1 ); } return ans; } }
位置为(i, j)的子数组的和为第j位的前缀和 - 第(i-1)位的前缀和。由此,维护一个存储前缀和频率的map,key为出现的前缀和,对应的value为出现的次数。对于一开始的情况,下标 0 之前没有元素,可以认为前缀和为 0,个数为 1 个,因此 preSumFreq.put(0, 1)。之后遍历数组,用sum存储当前的前缀和,若map中存在sum - k则说明符合条件的字串存在。之后更新前缀和map。
239. 滑动窗口最大值 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution { public int [] maxSlidingWindow(int [] nums, int k) { int n = nums.length; Deque<Integer> deque = new LinkedList <>(); int max[] = new int [n - k + 1 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++){ if (!deque.isEmpty() && deque.peekFirst() < i - k + 1 ){ deque.pollFirst(); } while (!deque.isEmpty() && nums[deque.peekLast()] < nums[i]){ deque.pollLast(); } deque.offerLast(i); if (i >= k - 1 ){ max[i - k + 1 ] = nums[deque.peekFirst()]; } } return max; } }
维护一个优先队列,队首为当前滑动窗口的最大值。i指针遍历整数数组,指针指到的数值视为当前滑动窗口的最右端,当队首元素(即最大值)已超过滑动窗口范围时移出队列,将要进队的元素与队中元素作比较,比其小的移出队列,因为现在的元素更新且更大,之前的元素已经不可能作为最大值。由于队列中存储的是序号且已从大到小排序,要移出的元素从队尾移除。最后将队头加入答案中。
76. 最小覆盖子串 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 class Solution { public String minWindow (String s, String t) { int m = s.length(), n = t.length(); if (m < n)return "" ; int len = Integer.MAX_VALUE, start = 0 ; HashMap<Character, Integer> freT = new HashMap <>(); HashMap<Character, Integer> freW = new HashMap <>(); for (char c : t.toCharArray()){ freT.put(c, freT.getOrDefault(c, 0 ) + 1 ); } int tCount = freT.keySet().size(); int left = 0 , right = 0 , have = 0 ; while (right < m){ char c = s.charAt(right); if (freT.containsKey(c)){ freW.put(c, freW.getOrDefault(c, 0 ) + 1 ); if (freW.get(c).equals(freT.get(c))) have++; while (have == tCount){ if (right - left + 1 < len){ len = right - left + 1 ; start = left; } char c_1 = s.charAt(left); if (freT.containsKey(c_1)){ freW.put(c_1, freW.get(c_1) - 1 ); if (freW.get(c_1) < freT.get(c_1)) have--; } left++; } } right++; } return len == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? "" : s.substring(start, start + len); } }
建立两张哈希表freT和freW,freT用来记录目标字符串的频率,freW用来记录源字符串的频率。tCount用来记录源字符串的去重后的字母的个数,have用来记录当前滑动窗口已满足的去重后的字母个数。用right指针遍历源字符串,left指针收缩窗口。当当前的滑动窗口已满足条件后(即have与tCount相等),比较检查是否需要更新当前长度与位置,之后收缩窗口,每次都判断是否需要更新,直到不满足条件。
普通数组 53. 最大子数组和 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution { public int maxSubArray (int [] nums) { int n = nums.length; int [] dp = new int [n]; dp[0 ] = nums[0 ]; int max = nums[0 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < n; i++){ dp[i] = Math.max(nums[i], dp[i - 1 ] + nums[i]); max = Math.max(dp[i], max); } return max; } }
使用动态规划算法,dp数组记录以当前位置i结尾的最大子数组和,分两种情况:继承前面的子数组,当前加在末尾变得更大了;继承后反而变小了,需要重新开始,以当前元素作为新的子数组。两者取大构造dp数组,最终dp的最大值即是数组的最大子数组和。
56. 合并区间 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution { public int [][] merge(int [][] intervals) { Arrays.sort(intervals, Comparator.comparingInt(a -> a[0 ])); int [][] merged = new int [intervals.length][2 ]; int mergedCount = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < intervals.length; i++) { if (mergedCount == 0 || intervals[i][0 ] > merged[mergedCount - 1 ][1 ]) { merged[mergedCount++] = intervals[i]; } else { merged[mergedCount - 1 ][1 ] = Math.max(merged[mergedCount - 1 ][1 ], intervals[i][1 ]); } } return Arrays.copyOf(merged, mergedCount); } }
对所有区间按区间开始位置排序,若有可能合并的数组则一定相邻,再遍历所有区间,若后面的区间开始位置小于或等于前面的区间结束位置则有重合,取两个区间的结束位置较大值作为合并后的区间的结束位置。
189. 轮转数组 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution { public void rotate (int [] nums, int k) { int n = nums.length; k %= n; reverse(nums, 0 , n - 1 ); reverse(nums, 0 , k - 1 ); reverse(nums, k, n - 1 ); } public void reverse (int [] nums, int start, int end) { while (start < end){ int temp = nums[start]; nums[start] = nums[end]; nums[end] = temp; start++; end--; } } }
先考虑k < n的情况,右移k次相当于先把数组整体翻转,再分别翻转前k位和后n - k位。当k ≥ n时,视为右移了k mod n次。
238. 除自身以外数组的乘积 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution { public int [] productExceptSelf(int [] nums) { int n = nums.length; int [] prePro = new int [n]; int [] sufPro = new int [n]; prePro[0 ] = 1 ; sufPro[n - 1 ] = 1 ; for (int i = 1 ; i < n; i++){ prePro[i] = prePro[i - 1 ] * nums[i - 1 ]; sufPro[n - 1 - i] = sufPro[n - i] * nums[n - i]; } int [] ans = new int [n]; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++){ ans[i] = prePro[i] * sufPro[i]; } return ans; } }
建立两个数组分别存放前缀积和后缀积,从1开始,前缀积数组第i个元素代表从第0个到第i-1个元素的积。原数组某个元素除自身以外数组的乘积等于对应位置前缀积和后缀积的乘积。
41. 缺失的第一个正数 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution { public int firstMissingPositive (int [] nums) { int n = nums.length; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++){ while (nums[i] > 0 && nums[i] <= n && nums[i] != nums[nums[i] - 1 ]){ int t = nums[i]; nums[i] = nums[t - 1 ]; nums[t - 1 ] = t; } } for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++){ if (nums[i] != i + 1 ){ return i + 1 ; } } return n + 1 ; } }
将原数组作为哈希表,定义数组长度为 N ,缺失的第一个整数一定在[1, N + 1]里,若这 N 个元素是连续正数,则答案是 N + 1,若不连续,则在[1, N]内一定存在缺失的正数。
矩阵 73. 矩阵置零 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution { public void setZeroes (int [][] matrix) { int row = matrix.length; int col = matrix[0 ].length; Set<Integer>zeroRowSet = new HashSet <>(); Set<Integer>zeroColSet = new HashSet <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < row; i++){ for (int j = 0 ; j < col; j++){ if (matrix[i][j] == 0 ){ zeroRowSet.add(i); zeroColSet.add(j); } } } for (int rowIndex : zeroRowSet){ for (int j = 0 ; j < col; j++) matrix[rowIndex][j] = 0 ; } for (int colIndex : zeroColSet){ for (int i = 0 ; i < row; i++) matrix[i][colIndex] = 0 ; } } }
遍历矩阵。将0元素对应的横纵坐标分别存储在set里,再分别遍历两个set把对应的行和列置零。
54. 螺旋矩阵 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 class Solution { public List<Integer> spiralOrder (int [][] matrix) { int totalRows = matrix.length; int totalCols = matrix[0 ].length; List<Integer> result = new ArrayList <>(); int top = 0 , right = totalCols - 1 , bottom = totalRows - 1 , left = 0 ; while (top <= bottom && left <= right) { for (int col = left; col <= right; col++) { result.add(matrix[top][col]); } top++; for (int row = top; row <= bottom; row++) { result.add(matrix[row][right]); } right--; if (top <= bottom) { for (int col = right; col >= left; col--) { result.add(matrix[bottom][col]); } bottom--; } if (left <= right) { for (int row = bottom; row >= top; row--) { result.add(matrix[row][left]); } left++; } } return result; } }
定义矩阵的四个边界,分四步螺旋遍历矩阵:从左到右遍历上边界,从上到下遍历右边界,从右到左遍历下边界,从下到上遍历左边界。完成一步后更新刚刚的边界。注意在遍历下边界和左边界时需要判断刚刚更新的边界是否仍满足继续遍历的条件。
48. 旋转图像 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution { public void rotate (int [][] matrix) { int row = matrix.length, col = matrix[0 ].length; for (int i = 0 ; i < row; i++){ for (int j = 0 ; j <= i; j++){ int t = matrix[i][j]; matrix[i][j] = matrix[j][i]; matrix[j][i] = t; } } for (int i = 0 ; i < row; i++){ for (int j = 0 ; j < col/2 ; j++){ int t = matrix[i][j]; matrix[i][j] = matrix[i][col - 1 - j]; matrix[i][col - 1 - j] = t; } } } }
将图像顺时针旋转 90 度相当于先把矩阵关于 -45° 的对角线翻转,再左右水平翻转。
240. 搜索二维矩阵 II 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution { public boolean searchMatrix (int [][] matrix, int target) { int row = matrix.length; int col = matrix[0 ].length; int x = 0 , y = col - 1 ; while (x < row && y >= 0 ){ if (matrix[x][y] == target) return true ; else if (matrix[x][y] > target) y--; else x++; } return false ; } }
将矩阵右上角作为搜索范围的初始右上角,左下角当作左下角。移动右上角位置,当右上角的元素等于target时返回。由于矩阵从左到右递增,从上到下递增,当右上角的元素大于target时,向左缩小范围;当右上角的元素小于target时,向下缩小范围。若直到缩小到矩阵左下角的元素仍找不到target,则不存在。
链表 160. 相交链表 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 public class Solution { public ListNode getIntersectionNode (ListNode headA, ListNode headB) { Set<ListNode>setA = new HashSet <>(); ListNode p1 = headA, p2 = headB; while (p1 != null ){ setA.add(p1); p1 = p1.next; } while (p2 != null ){ if (setA.contains(p2)) return p2; else p2 = p2.next; } return null ; } }
遍历链表A,把其中节点都添加到集合中。再遍历链表B,当链表B节点存在于A的集合中时则两链表相交。
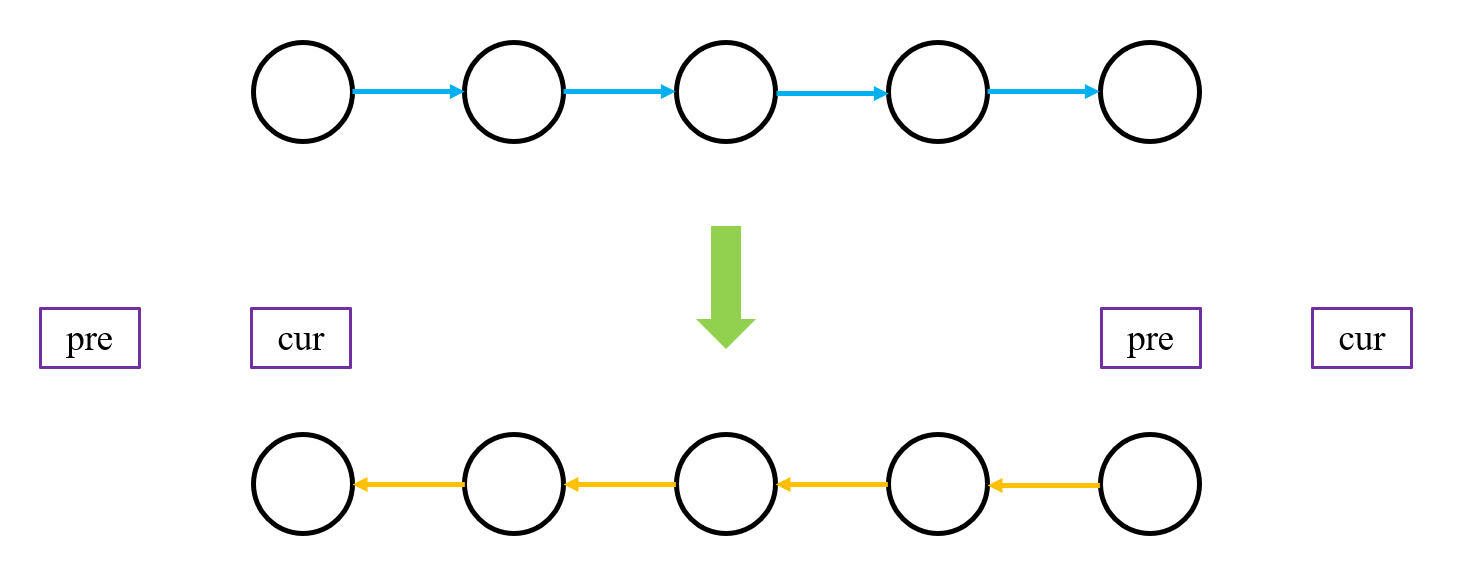
206. 反转链表 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution { public ListNode reverseList (ListNode head) { ListNode pre = null ; ListNode cur = head; while (cur != null ){ ListNode next = cur.next; cur.next = pre; pre = cur; cur = next; } return pre; } }
234. 回文链表 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 class Solution { public boolean isPalindrome (ListNode head) { if (head == null || head.next == null ) { return true ; } ListNode slow = head; ListNode fast = head; int count = 0 ; ListNode preSlow = slow; while (fast != null && fast.next != null ){ preSlow = slow; slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next.next; count++; } ListNode p1 = preSlow; ListNode p2 = new ListNode (); if (fast != null ) p2 = slow.next; else p2 = slow; ListNode reversedHead = reverseList(slow); p1 = head; p2 = reversedHead; while (p1 != null && p2 != null ){ if (p1.val != p2.val) return false ; p1 = p1.next; p2 = p2.next; } return true ; } private ListNode reverseList (ListNode head) { ListNode pre = null ; ListNode cur = head; while (cur != null ){ ListNode next = cur.next; cur.next = pre; pre = cur; cur = next; } return pre; } }
利用快慢指针得到链表的中间位置,再把后半段链表反转,反转后用两个指针同时遍历前半段和反转后的后半段,如果遇到不一样的则不是回文链表。
141. 环形链表 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 public class Solution { public boolean hasCycle (ListNode head) { if (head == null || head.next == null ) return false ; ListNode slow = head; ListNode fast = head; while (slow != null && fast != null && fast.next != null ){ slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next.next; if (slow == fast) return true ; } return false ; } }
用快慢指针遍历链表,两个指针速度差值为1,若有环则两个指针一定能相遇。
142. 环形链表 II 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 public class Solution { public ListNode detectCycle (ListNode head) { if (head == null || head.next == null ) return null ; ListNode slow = head; ListNode fast = head; while (slow != null && fast != null && fast.next != null ){ slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next.next; if (slow == fast) { ListNode a = head; while (a != slow){ a = a.next; slow = slow.next; } return a; } } return null ; } }
判断是否有环部分同上题。若有环,再在头节点放置一个指针开始和slow指针同时遍历,当两指针相遇时则是环的入口。
21. 合并两个有序链表 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 class Solution { public ListNode mergeTwoLists (ListNode list1, ListNode list2) { ListNode head = new ListNode (-1 ); ListNode ptr = head; ListNode p1 = list1; ListNode p2 = list2; while (p1 != null && p2 != null ){ if (p1.val <= p2.val){ ptr.next = p1; p1 = p1.next; } else { ptr.next = p2; p2 = p2.next; } ptr = ptr.next; } if (p1 == null ) { ptr.next = p2; } else { ptr.next = p1; } return head.next; } }
利用两个指针分别在两个链表中移动,指针ptr指向当前合并后的链表的末尾,next指向当前指针中的较小值。当有一个链表遍历完后循环停止,再把ptr指向还未遍历结束的链表。
2. 两数相加 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 class Solution { public ListNode addTwoNumbers (ListNode l1, ListNode l2) { ListNode ptr = new ListNode (0 ); ListNode head = ptr; int carry = 0 ; while (l1 != null || l2 != null ) { int x = (l1 != null ) ? l1.val : 0 ; int y = (l2 != null ) ? l2.val : 0 ; int sum = x + y + carry; carry = sum / 10 ; ptr.next = new ListNode (sum % 10 ); ptr = ptr.next; if (l1 != null ) l1 = l1.next; if (l2 != null ) l2 = l2.next; } if (carry > 0 ) { ptr.next = new ListNode (carry); } return head.next; } }
利用两个指针分别在两个链表中移动,两数以及carry相加得到的结果存在一个新节点中,若两数相加产生进位则把carry置1。当有两个链表都遍历完后循环停止,若最后carry还有未完成的进位则再新建一个值为1的节点到答案链表的末尾。
19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 class Solution { public ListNode removeNthFromEnd (ListNode head, int n) { ListNode n1 = head; ListNode n2 = head; ListNode pre = new ListNode (); int count = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { n1 = n1.next; count++; } while (n1 != null ){ n1 = n1.next; pre = n2; n2 = n2.next; count++; } if (count == n) return head.next; pre.next = n2.next; return head; } }
利用快慢指针,快指针先移动到第 n 位,再把慢指针从头与快指针一起移动,当快指针到链表末尾时,快指针就到了n - k + 1的位置,指向要删除的节点。用 count 计数链表长度,若 n 与 count 相等,则要删除的节点是第一个节点,返回头节点的下一个节点;若不相等则还是返回最初的头节点。
24. 两两交换链表中的节点 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class Solution { public ListNode swapPairs (ListNode head) { if (head == null || head.next == null ) return head; ListNode h = new ListNode (0 , head); ListNode t = h; while (t.next != null && t.next.next != null ){ ListNode p1 = t.next; ListNode p2 = t.next.next; p1.next = p2.next; p2.next = p1; t.next = p2; t = t.next.next; } return h.next; } }
建立一个虚拟头节点 h ,h.next 指向 head,用指针 t 从 h 开始遍历链表,用双指针 p1、p2 成对遍历链表,三个指针的顺序从 t -> p1 -> p2 变成 t -> p2 -> p1。当三个指针都不为空时交换 p1 和 p2,再把 t 往后移两个节点继续两两交换(已在循环条件保证 t 移动后也不为空)。最后返回虚拟头节点的下一个节点,即交换后的真正头节点。
25. K 个一组翻转链表 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 class Solution { public ListNode reverseKGroup (ListNode head, int k) { if (head == null || k <= 1 ) return head; ListNode dummy = new ListNode (0 , head); ListNode p1 = dummy, p2 = dummy; while (true ) { int count = 0 ; while (count < k && p2 != null ) { p2 = p2.next; count++; } if (p2 == null ) break ; ListNode nextGroupHead = p2.next; ListNode[] reversed = reverseList(p1.next, p2); p1.next = reversed[0 ]; reversed[1 ].next = nextGroupHead; p1 = reversed[1 ]; p2 = p1; } return dummy.next; } public ListNode[] reverseList(ListNode head, ListNode tail) { ListNode prev = tail.next; ListNode p = head; while (prev != tail) { ListNode nex = p.next; p.next = prev; prev = p; p = nex; } return new ListNode []{tail, head}; } }
先把之前反转链表 改造成输入链表的头尾节点,返回反转过后的头尾节点。再用快慢指针 p1、p2 遍历链表,p2先行分组,每经过 K 个节点就进行一次分组的反转,之后更新 p1、p2 到反转过后的分组末尾。若 p2 走过剩下的节点不足够进行分组就结束遍历。
138. 随机链表的复制 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 class Solution { Map<Node, Node> map = new HashMap <Node, Node>(); public Node copyRandomList (Node head) { if (head == null ) return null ; if (!map.containsKey(head)) { Node newNode = new Node (head.val); map.put(head, newNode); newNode.next = copyRandomList(head.next); newNode.random = copyRandomList(head.random); } return map.get(head); } }
利用全局 map 记录当前已构建的节点。再使用递归方法,当传入的节点为空时返回空,当不为空且 map 里还未记录时建立新节点,存入 map 并递归进入 next 和random 进行复制。
148. 排序链表 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 class Solution { public ListNode sortList (ListNode head) { return sortList(head, null ); } public ListNode sortList (ListNode head, ListNode tail) { if (head == tail || head.next == tail) { if (head != null ) head.next = null ; return head; } ListNode slow = head, fast = head; while (fast != tail) { slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next; if (fast != tail) fast = fast.next; } ListNode l1 = sortList(head, slow); ListNode l2 = sortList(slow, tail); return mergeTwoLists(l1, l2); } public ListNode mergeTwoLists (ListNode list1, ListNode list2) { ListNode head = new ListNode (-1 ); ListNode ptr = head; ListNode p1 = list1; ListNode p2 = list2; while (p1 != null && p2 != null ){ if (p1.val <= p2.val){ ptr.next = p1; p1 = p1.next; } else { ptr.next = p2; p2 = p2.next; } ptr = ptr.next; } if (p1 == null ) { ptr.next = p2; } else { ptr.next = p1; } return head.next; } }
利用归并排序思想,并使用之前的合并两个有序列表 ,通过递归将链表自上到下两两分割直到只剩一个或没有节点,再进行合并,返回合并后的链表首节点。在分割链表时,使用快慢指针确定链表的中间节点和末尾节点的位置。
23. 合并 K 个升序链表 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 class Solution { public ListNode mergeKLists (ListNode[] lists) { if (lists.length == 0 ) return null ; while (lists.length > 1 ) { List<ListNode> temp = new ArrayList (); for (int i = 0 ; i < lists.length; i+=2 ) { ListNode l1 = lists[i]; ListNode l2 = null ; if (i + 1 < lists.length) l2 = lists[i + 1 ]; temp.add(mergeTwoLists(l1, l2)); } lists = temp.toArray(new ListNode [0 ]); } return lists[0 ]; } public ListNode mergeTwoLists (ListNode list1, ListNode list2) { ListNode head = new ListNode (-1 ); ListNode ptr = head; ListNode p1 = list1; ListNode p2 = list2; while (p1 != null && p2 != null ){ if (p1.val <= p2.val){ ptr.next = p1; p1 = p1.next; } else { ptr.next = p2; p2 = p2.next; } ptr = ptr.next; } if (p1 == null ) { ptr.next = p2; } else { ptr.next = p1; } return head.next; } }
使用之前的合并两个有序列表 ,将链表两两组合进行合并,当合并后的 list 中的链表数量仍大于一时继续进行组合合并,直到只剩一个链表。
146. LRU 缓存 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 class LRUCache { private int capacity; private LinkedList<Integer> list; private Map<Integer, Integer> map; public LRUCache (int capacity) { this .capacity = capacity; this .list = new LinkedList <>(); this .map = new HashMap <>(); } public int get (int key) { if (map.containsKey(key)) { list.remove(Integer.valueOf(key)); list.add(key); return map.get(key); } else return -1 ; } public void put (int key, int value) { if (map.containsKey(key)){ map.put(key, value); list.remove(Integer.valueOf(key)); list.add(key); } else if (list.size() < capacity) { map.put(key, value); list.add(key); } else { Integer removedValue = list.removeFirst(); map.remove(removedValue); list.add(key); map.put(key, value); } } }
建立 map 记录缓存中存放的 key-value,链表存放缓存中关键字使用的频率,越久未使用则放得越前。当要取出关键字时,先在 map 中检查是否存在,若存在则取出,并在链表中把该组移动到最末端,表示最近使用。当要存放关键字时,先在 map 中检查是否存在,若存在则直接更改,并更新链表中的位置;若不存在则判断容量是否已满,容量已满就在链表和 map 中移除链表最前的关键字,之后再在链表和 map 中进行插入。
二叉树 94. 二叉树的中序遍历 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution { public List<Integer> inorderTraversal (TreeNode root) { List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList <Integer>(); inorder(root, ans); return ans; } public void inorder (TreeNode root, List<Integer> ans) { if (root == null ) return ; inorder(root.left, ans); ans.add(root.val); inorder(root.right, ans); } }
104. 二叉树的最大深度 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution { public int maxDepth (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) return 0 ; int left = maxDepth(root.left); int right = maxDepth(root.right); return Math.max(left, right) + 1 ; } }
使用递归,终止条件是遍历到空节点时返回深度为0,依次求出左子树和右子树的高度并取较大值加1就是当前节点的深度。
226. 翻转二叉树 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class Solution { public TreeNode invertTree (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) return root; TreeNode left = invertTree(root.left); TreeNode right = invertTree(root.right); root.left = right; root.right = left; return root; } }
利用递归,分别构造出当前节点的左右子树再返回。
101. 对称二叉树 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class Solution { public boolean isSymmetric (TreeNode root) { return check(root.left, root.right); } public boolean check (TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { if (p == null && q == null ) return true ; if (p == null || q == null ) return false ; return p.val == q.val && check(p.right, q.left) && check(p.left, q.right); } }
利用递归,终止条件是两节点至少有一个为空时。
543. 二叉树的直径 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 class Solution { int ans = -1 ; public int diameterOfBinaryTree (TreeNode root) { maxDepth(root); return ans; } public int maxDepth (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) return 0 ; int left = maxDepth(root.left); int right = maxDepth(root.right); ans = Math.max(ans, left + right); return Math.max(left, right) + 1 ; } }
与求二叉树的最大深度 思路类似,经过某个节点最长路径的长为其左子树的最长路径与右子树最长路径之和,再对 ans 进行更新,返回左右子树最长路径的较大值加一作为经过当前节点的最长单侧路径。
102. 二叉树的层序遍历 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder (TreeNode root) { List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList <List<Integer>>(); if (root == null ) return ans; Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList <TreeNode>(); queue.offer(root); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { int num = queue.size(); List<Integer> t = new ArrayList <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < num; i++) { TreeNode node = queue.poll(); t.add(node.val); if (node.left != null ) queue.offer(node.left); if (node.right != null ) queue.offer(node.right); } ans.add(t); } return ans; } }
利用队列,每次进队同一层的节点,再对该层每个节点的子节点进队并记录节点的值,然后进行出队。为了实现分层,还须每次记录当层节点的个数,每次只出队当层节点。
108. 将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution { public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST (int [] nums) { return sort(nums, 0 , nums.length - 1 ); } private TreeNode sort (int [] nums, int left, int right) { if (left > right) return null ; int mid = (left + right) / 2 ; TreeNode node = new TreeNode (nums[mid]); node.left = sort(nums, left, mid - 1 ); node.right = sort(nums, mid + 1 , right); return node; } }
利用递归,每次对数组对半分割,每次构建以中间节点为根节点的树,并返回中间节点。
98. 验证二叉搜索树 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class Solution { public boolean isValidBST (TreeNode root) { return isValidBST(root, Long.MIN_VALUE, Long.MAX_VALUE); } private boolean isValidBST (TreeNode root, long min, long max) { if (root == null ) return true ; if (root.val <= min ||root.val >= max) return false ; return isValidBST(root.left, min, root.val) && isValidBST(root.right, root.val, max); } }
利用递归,每次限定当前子树的最小值和最大值,当出现根节点不是大于最小值且小于最大值的情况时则可以判断不是二叉搜索树。对于左子树,最小值仍为当前树的最小值,最大值则为当前根节点的值;对于右子树,最小值为当前根节点的值,最大值则为当前树的最大值。